Reportedly, the energy efficiency of the Intel Sierra Forest chip is expected to more than double.
The American company claims that its Intel Sierra Forest chip will have up to 240 percent better performance per watt than its current generation of chips for large data center products. This, he says, will increase energy efficiency, which is part of the industry's broader effort to reduce electricity consumption.
At a conference on semiconductor technology in Silicon Valley, the company said that the Intel Sierra Forest chip will do more than double the computing work that can be done for every watt of power used, writes Reuters.
The data centers that power the Internet and online services consume huge amounts of electricity, and technology firms face pressure to remain stable or reduce the amount of energy they use. That's what has led semiconductor designers and manufacturers to focus on how to make them that will do more computing work per chip.
Ampere Computing, a startup founded by former Intel executives, is the first to market with a chip focused on efficiently handling cloud computing operations. Intel and its rival AMD followed suit by announcing similar products, and AMD's offer has been on the market since June this year.
 Intel
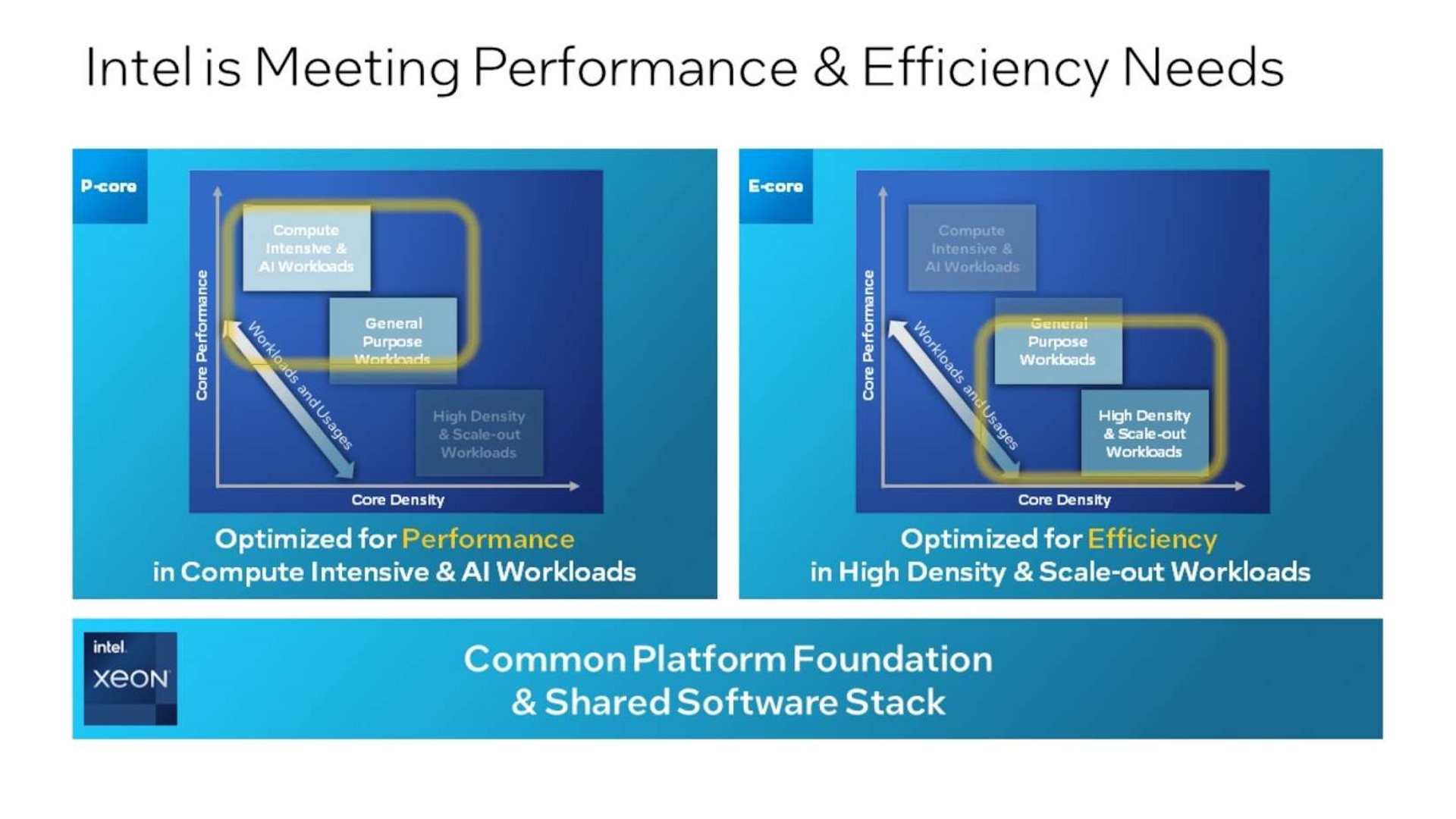
IntelIntel, which has lost market share to the two companies in data centers, said on Monday that its upcoming chip for this purpose is on track to reach rivals within the next year. Intel Sierra Forest will not be the only chip intended for data centers, but will be followed later in 2024 by the Granite Rapids chip. The latter will be more focused on performance, but will consume more energy, while the Sierra Forest will be more efficient.
The company's representatives pointed out that their partners can save energy by moving something that works on five, 10 or 15 different nodes into one new chip.
Both of these chips will be manufactured on the Intel 3 manufacturing process (formerly known as 5 nm) of the second generation that uses EUV lithography. In reality, it is an improved Intel 4 (7nm) manufacturing process. It should provide a design with a higher packing density of electronic circuits that provides high performance, but also lower resistance and higher current.